Now that we have an understanding of what light is and why it is
important to astronomy, how do astronomers study the light from stars and
other celestial bodies? The telescope is the principal tool of the astronomer,
and its primary function is to
Although, telescopes used at different wavelengths are very different,
the information that we want from them are the same, and they all have
some common characteristics.
2.
What factors influence a telescope's LGP?
For example, we usually talk about relative Light Gathering Power:
So, we have the First Rule of Telescope Design:
For example, the exposure time of the Human Eye
Note, this is why it can be somewhat disappointing when you actually look through a telescope. The images in books and other publications are almost always time exposure images of faint objects, sometimes several hours.
Minimum Angle of Resolution =
For Example, the 5 meter Hale Telescope:
So, the Second Rule of Telescope Design:
What other factor limits the resolution of ground-based telescopes?
Problems with Refractors:
What shape must the mirror be?
Reflector Designs:
For example, the Keck Telescope in Hawaii:
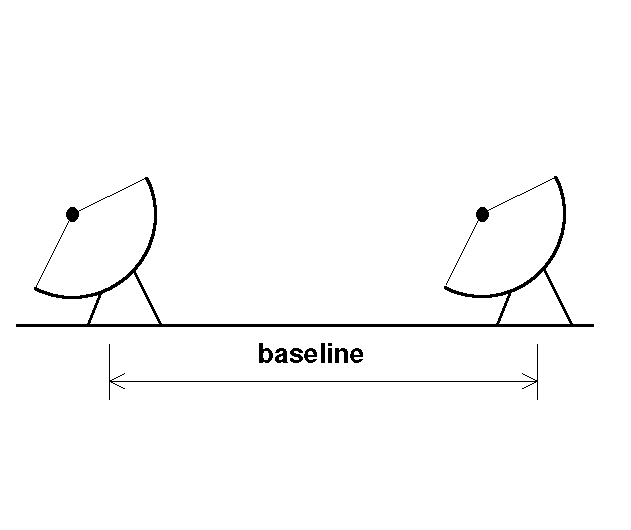
Radio Telescopes are big metallic dishes that focus radio waves to
a common focus, but the big problem with Radio Telescopes is

| This document was last modified on Thursday, 04-Feb-1999 17:22:56 EST
and has been accessed [an error occurred while processing this directive] times.
Send comments or suggestions to: |